2010
| News | Registration | Abstracts | Accommodation | Excursions | Deadlines | Organizing committee |
| First circular | Participants | Abstract submission | Travel | Program | Seminar History | Contact us |
| Новости |
| Первый циркуляр |
| Регистрация |
| Оформление тезисов |
| Тезисы |
| Программа |
| Участники |
| Размещение |
| Экскурсии |
| Проезд |
| Важные даты |
| Оргкомитет |
| Обратная связь |
Paragenetic relations of diamond with silicate and carbonate minerals
in the system carbonatite-diamond (experiment at 8.5 GPa)
Spivak A.V., Litvin J.A.
Institute of Experimental Mineralogy of RAS, 142432 Chernogolovka, the Moscow region
e-mail: spivak@iem.ac.ru
Experimental researches of melting phase relations of diamond and syngenetic minerals in multicomponent system natural carbonatite - diamond were carried out at pressure 8.5 GPa and temperatures 1300 - 1800оС (PT-conditions of thermodynamic stability of diamond). Natural carbonatite of the Chagatai complex (Uzbekistan) gets a mineralization of high-Ca eclogite – grospydites under these conditions. Melting phase diagram of the system was studied and “syngenesis diagram” constructed. The curve of solubility of diamond in completely miscible carbonate-silicate melts (values of solubility - within 15 - 18 wt. % carbon) is of great importance in the syngenesis diagram. The curve of diamond solubility divides the phase diagram into two fields: (1) phase relations with participation nonsaturated to diamond melts-solutions of carbon, liquidus phase is garnet (area of diamond dissolution) and (2) phase relations with participation of saturated to diamond melts-solutions, liquidus phase is diamond (area of diamond crystallization). Diamond bearing phase associations diamond + garnet + melt, diamond + garnet + clinopyroxene + melts, diamond + garnet + clinopyroxene + carbonate + melts and as a result subsolidus association diamond + garnet + clinopyroxene + carbonate are formed from carbonate-silicate melts at temperature lowering in the field of diamond crystallization.
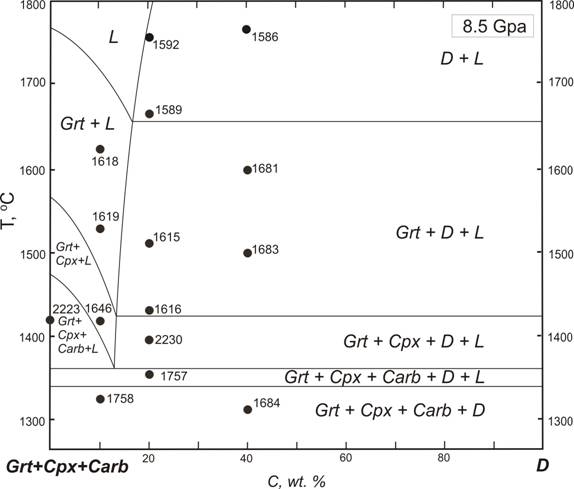
The experimental data testifies the paragenetic nature of silicate and carbonate minerals, crystallized with diamond. Physico-chemical mechanism of diamond formation in carbonate-silicate melts is demonstrated. Analysis of physical and chemical behavior of natural diamond-forming magma chamber is given on the basis of the syngenesis phase diagram.
This study was financially supported by RFBR grant 08-05-00110, 10-05-00110 and grants of the president RF МК-4754.2009.5, МК-4735.2009.5.